Contents
Introduction
William James was a pioneering American psychologist and philosopher, widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the history of psychology. Known as the “Father of American Psychology,” James’ work laid the foundation for modern psychology and significantly contributed to the development of pragmatism and functionalism. His profound insights into human consciousness, emotion, and behavior have left an enduring legacy in both psychology and philosophy.

In this article, we will Research William James’ groundbreaking contributions to psychology and philosophy, examining his key theories and the lasting impact of his work on modern thought and practices.
Early Life and Education
William James was born on January 11, 1842, in New York City, into a wealthy and intellectually prominent family. His father, Henry James Sr., was a theologian and philosopher, and his younger brother, Henry James, became a renowned novelist. Growing up in an environment that encouraged intellectual exploration, James was exposed to a broad array of ideas and disciplines from an early age.
Image Source: William James, 1880, by J. Notman, Boston (photographer). (Houghton Library at Harvard University; public domain via Wikimedia Commons)

Developing fluency in multiple languages and a deep appreciation for different cultures. His family’s frequent travels and his exposure to diverse intellectual traditions greatly influenced his thinking and academic pursuits.
Educational Journey
| Aspect | Details |
| Early Education | James received a broad and diverse education, attending schools in Europe and the United States. His early education was heavily influenced by his father’s intellectual interests. |
| Harvard University | James initially enrolled at Harvard to study art but later switched to scientific studies, earning a medical degree in 1869. |
| Medical Studies | Despite earning a medical degree, James never practiced medicine. Instead, he pursued a career in psychology and philosophy, driven by his interest in the human mind and behavior. |
| Academic Career | James began his academic career at Harvard, where he taught physiology, psychology, and philosophy. His teaching and writing significantly influenced the development of psychology as a scientific discipline in the United States. |
Timeline of Early Influences
| Aspect | Details |
| Charles Darwin | Darwin’s theory of evolution had a profound impact on James’ thinking, particularly his views on the adaptive functions of consciousness and behavior. |
| René Descartes | Descartes’ philosophy and emphasis on doubt and inquiry influenced James’ approach to psychology and philosophy. |
| John Stuart Mill | Mill’s utilitarianism and emphasis on empirical evidence shaped James’ pragmatic approach to philosophy and psychology. |
| Hermann von Helmholtz | Helmholtz’s work in physiology and psychology provided a scientific foundation for James’ studies of the mind and behavior. |
Major Theories and Works

Pragmatism
William James was a key figure in the development of pragmatism, a philosophical movement that evaluates theories and beliefs based on their practical effects and utility. Key elements include:
- Practical Consequences: Pragmatism assesses the truth of ideas by their practical consequences and their ability to solve problems, emphasizing the usefulness of concepts in real-world applications.
- Dynamic and Evolving Beliefs: The philosophy posits that beliefs and theories are not static but evolve based on their effectiveness in addressing issues and adapting to new experiences.
- Focus on Experience: Pragmatism values human experience and the practical impact of ideas, suggesting that meaning and truth are rooted in their practical implications rather than abstract principles.
Image Source: allegralaboratory.net
Functionalism
William James played a key role in the development of functionalism, a major school of thought in psychology that focuses on the functions and purposes of the mind and behavior in adapting to the environment. Key elements include:
- Purpose of Behavior: Functionalism emphasizes understanding the purpose of mental processes and behavior, exploring how they help individuals adapt and survive in their environment.
- Adaptation and Evolution: The theory highlights the role of mental processes in helping organisms adapt to their surroundings, drawing on principles of evolution and natural selection.
- Focus on Practical Applications: Functionalism is concerned with the practical application of psychological knowledge, including how mental processes influence learning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
Image Source: specialeducationnotes.co.in
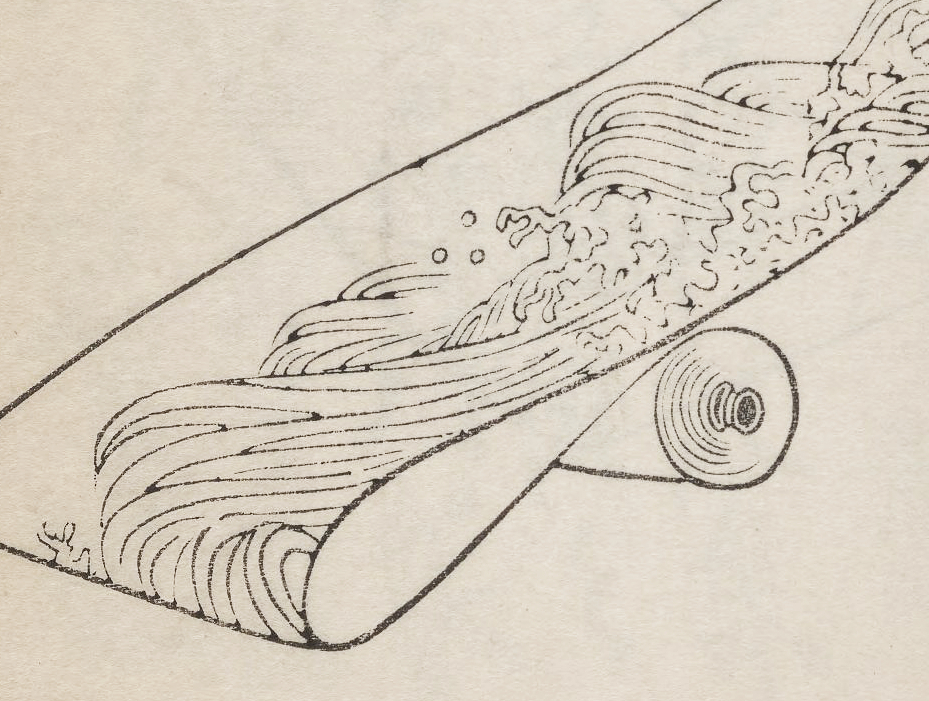
The Stream of Consciousness
William James introduced the concept of the “stream of consciousness,” a fundamental idea in psychology that describes the continuous flow of thoughts and feelings in the human mind. Key elements include:
- Continuous Flow: The theory asserts that consciousness is not a series of discrete thoughts but a continuous and fluid stream, reflecting the constant, ever-changing nature of human experience.
- Personal and Dynamic: According to James, each individual’s stream of consciousness is unique and dynamic, shaped by personal experiences, thoughts, and emotions, which flow seamlessly from one to another.
- Focus on Subjective Experience: The concept emphasizes the importance of subjective experience, highlighting how personal perceptions and mental states contribute to the overall flow of consciousness.
Image Source: publicdomainreview.org
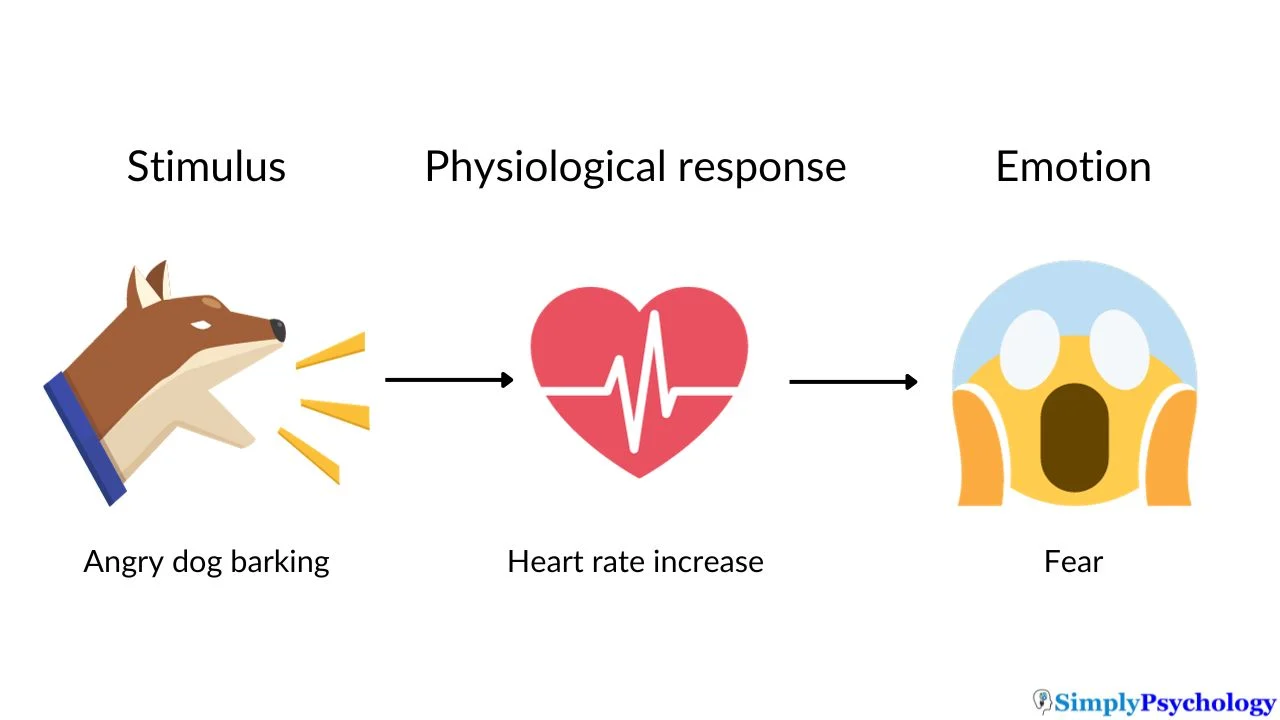
The James-Lange Theory of Emotion
William James and Carl Lange independently proposed the James-Lange Theory of Emotion, which suggests that emotions result from physiological responses to stimuli. Key elements include:
- Physiological Responses: The theory posits that emotions are experienced after the body reacts to an external stimulus, such as changes in heart rate or muscle tension.
- Emotion as a Result of Bodily Changes: According to the theory, we perceive emotions because we notice our physiological changes, such as trembling or sweating, which we then interpret as specific emotions.
- Sequential Process: The theory outlines a sequential process where physiological arousal occurs first, followed by the emotional experience, challenging earlier ideas that emotions precede physiological responses.
Image Source: simplypsychology.org
Psychologists Influenced by James
- John Dewey – A prominent philosopher and psychologist, Dewey’s work in education and pragmatism was heavily influenced by James’ theories. Dewey’s emphasis on experiential learning and the practical application of knowledge reflects James’ pragmatic approach (Dewey, 1938).
- G. Stanley Hall – A pioneering psychologist and educator, Hall was influenced by James’ functionalist perspective and contributed to the development of educational psychology and child development (Hall, 1904).
- Edward Thorndike – Known for his work on learning theory and educational psychology, Thorndike was inspired by James’ focus on the adaptive functions of behavior and the importance of empirical research (Thorndike, 1913).
- Carl Rogers – A key figure in humanistic psychology, Rogers’ emphasis on personal experience and self-actualization was influenced by James’ focus on the individual and the stream of consciousness (Rogers, 1961).
- B.F. Skinner – Although a behaviorist, Skinner’s work on operant conditioning and behavior modification was influenced by James’ pragmatic approach to psychology and emphasis on the practical applications of research (Skinner, 1953).
Impact on Psychology
- Influence on Modern Thought: William James’ ideas have had a profound impact on various fields within psychology, including educational psychology, clinical psychology, and the psychology of religion. His pragmatic approach and emphasis on the practical consequences of ideas have influenced both theoretical and applied psychology, promoting a focus on outcomes and real-world applications. James’ work has also had a lasting impact on philosophy, particularly through the development of pragmatism and functionalism.
- Contributions to Related Fields: James’ interdisciplinary approach extended his influence to areas such as education, philosophy, and religious studies. His emphasis on the adaptive functions of behavior and the importance of individual experiences has informed educational practices, therapeutic approaches, and the study of religious and mystical experiences. James’ work has also influenced the development of existential and humanistic psychology, emphasizing the significance of personal meaning and individual agency.
Legacy and Influence
Long-Term Impact
William James’ legacy endures through his lasting contributions to psychology and philosophy. His pioneering work in pragmatism, functionalism, and the study of consciousness has provided a foundation for numerous subsequent theories and research. James’ emphasis on the practical applications of ideas and the importance of individual experiences continues to influence contemporary psychology and philosophy, highlighting the enduring relevance of his work.
Recognition and Honors
James received numerous accolades and recognition for his work, including honorary degrees and prestigious awards. He was a founding member of the American Psychological Association and served as its president. James’ contributions to psychology and philosophy have been commemorated in various institutions and awards, underscoring his significant impact on these fields. His legacy is also preserved through the many students he mentored and the continued study and application of his theories.
Criticism and Controversies
While William James has garnered significant recognition for his contributions to psychology and philosophy, his work has not been without criticism. Some argue that his pragmatic approach can be overly simplistic, neglecting the complexities and nuances of human cognition and emotion. Critics also point out that James’ focus on individual experiences and subjective phenomena may lack the empirical rigor that other approaches in psychology strive for. Despite these criticisms, James’ innovative ideas and methodologies have left an indelible mark on the fields he contributed to, continuing to inspire debate and further research.
Conclusion
William James’ life and work have profoundly shaped the fields of psychology and philosophy. His theories on pragmatism, functionalism, and the stream of consciousness offer valuable insights into human behavior and cognition. By emphasizing the practical applications of ideas and the importance of individual experiences, James has provided a comprehensive framework for understanding and enhancing human experience. As his legacy continues to unfold, James’ contributions to psychology and philosophy will likely inspire future generations of researchers, educators, and practitioners.
Bibliography
- [1] Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The Exercise of Control. New York: W.H. Freeman.
- [2] Beck, A. T. (1979). Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders. New York: Penguin.
- [3] Ellis, A. (1962). Reason and Emotion in Psychotherapy. New York: Lyle Stuart.
- [4] Hall, G. S. (1904). Adolescence: Its Psychology and Its Relations to Physiology, Anthropology, Sociology, Sex, Crime, Religion and Education. New York: D. Appleton & Company.
- [5] James, W. (1890). The Principles of Psychology. New York: Henry Holt and Company.
- [6] James, W. (1902). The Varieties of Religious Experience: A Study in Human Nature. New York: Longmans, Green, and Co.
- [7] James, W. (1907). Pragmatism: A New Name for Some Old Ways of Thinking. New York: Longmans, Green, and Co.
- [8] Lazarus, R. S. (1991). Emotion and Adaptation. New York: Oxford University Press.
- [9] Mischel, W. (1968). Personality and Assessment. New York: Wiley.
- [10] Rotter, J. B. (1954). Social Learning and Clinical Psychology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- [11] Skinner, B. F. (1953). Science and Human Behavior. New York: Macmillan.
- [12] Thorndike, E. L. (1913). Educational Psychology: The Psychology of Learning. New York: Teachers College, Columbia University.






