Contents
Introduction
Max Wertheimer was a pioneering psychologist best known for founding Gestalt psychology, a movement that fundamentally transformed our understanding of perception and cognitive processes. Wertheimer’s work emphasized the holistic nature of perception, arguing that we perceive objects and patterns as whole units rather than as a sum of their parts. His theories have had a profound impact on various fields, including psychology, education, and design, making him one of the most influential figures in the history of psychology.

In this article, we will review Max Wertheimer’s contributions to Gestalt psychology, his revolutionary ideas on perception, and the lasting impact of his theories on psychology, education, and design.
Early Life and Education
Max Wertheimer was born on April 15, 1880, in Prague, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (now the Czech Republic). He was raised in an intellectually stimulating environment, as his father, Wilhelm Wertheimer, was a successful educator and his mother, Rosa, was a cultured and artistic woman. Growing up in a household that valued education and intellectual curiosity, Wertheimer developed a strong interest in music, literature, and philosophy from an early age.
Image Source: gestalttherapyblog.com

Educational Journey
| Aspect | Details |
| Early Education | Wertheimer attended classical secondary schools in Prague, where he developed a strong foundation in the humanities and sciences. |
| University of Prague | Wertheimer began his higher education at the University of Prague, where he initially studied law before switching to philosophy and psychology. |
| University of Berlin | He continued his studies at the University of Berlin, where he was influenced by prominent psychologists and philosophers, including Carl Stumpf. |
| University of Würzburg | Wertheimer completed his doctoral studies at the University of Würzburg under the supervision of Oswald Külpe, earning his Ph.D. in 1904 with a dissertation on psychological aspects of music. |
| Research | Wertheimer conducted early research on the psychology of music and the perception of rhythm, which laid the groundwork for his later work on Gestalt psychology. |
Timeline of Early Influences
| Aspect | Details |
| Carl Stumpf | Stumpf’s work on the psychology of music and auditory perception significantly influenced Wertheimer’s early research interests. |
| Oswald Külpe | Külpe’s experimental methods and focus on higher mental processes shaped Wertheimer’s approach to psychological research. |
| Christian von Ehrenfels | Ehrenfels’ concept of “Gestalt qualities” provided a theoretical foundation for Wertheimer’s later work on Gestalt psychology. |
| Albert Einstein | Wertheimer’s friendship with Einstein and their discussions on the nature of perception and reality influenced his thinking on holistic perception. |
Major Theories and Works

Gestalt psychology
Max Wertheimer, the founder of Gestalt psychology, introduced a revolutionary approach to understanding perception and cognition. Key elements include:
- Holistic Perception: Gestalt psychology posits that the mind perceives objects and patterns as complete, unified wholes rather than merely as the sum of individual sensory elements. This holistic view challenges traditional theories that emphasize linear and additive processes in perception.
- Figure-Ground Relationship: A central concept in Gestalt psychology is the figure-ground relationship, which describes how we instinctively separate elements of a visual field into the main focus (figure) and the background (ground).
Image Source: psychologs.com
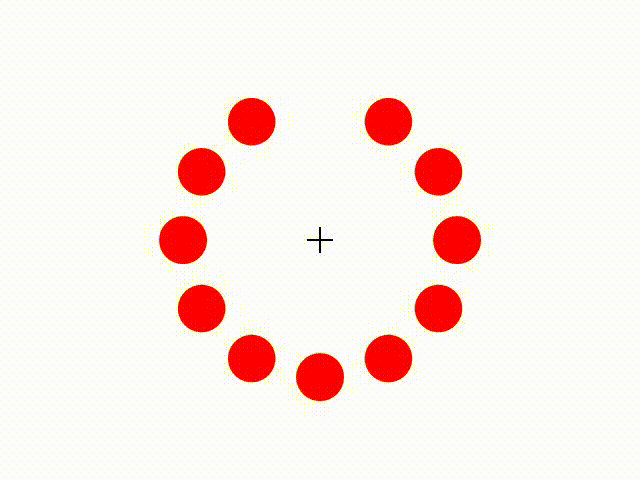
The Phi Phenomenon
The Phi Phenomenon, discovered by Max Wertheimer, is a foundational concept in Gestalt psychology that explains how we perceive motion. Key elements include:
- Illusion of Motion: The Phi Phenomenon describes how the human mind perceives a sequence of static images, shown in rapid succession, as continuous motion. This illusion underpins our experience of watching movies or animated images.
- Challenging Associationism: Wertheimer’s discovery of the Phi Phenomenon challenged the associationist view, which suggested that motion perception was merely the result of combining successive images. Instead, Gestalt psychology emphasized that the mind actively constructs motion from still images.
Image Source: deviantart.com
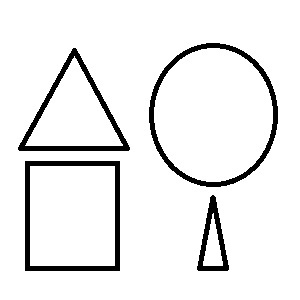
Principles of Perceptual Organization
Wertheimer identified several principles of perceptual organization that explain how we perceive visual elements as unified wholes. These principles include:
- Proximity: Elements that are close to each other are perceived as belonging together.
- Similarity: Elements that are similar in appearance are perceived as part of the same group.
- Continuity: Elements arranged in a line or curve are perceived as continuing in a particular direction.
- Closure: The mind tends to fill in missing information to perceive a complete image.
- Figure-Ground: Elements are perceived as either the figure (the main object of focus) or the ground (the background).
Image Source: study.com

Productive Thinking
Max Wertheimer’s concept of Productive Thinking is a key aspect of Gestalt psychology and focuses on how individuals solve problems and create novel solutions. Key aspects include:
- Insightful Problem Solving: Productive Thinking involves solving problems through insight, where individuals suddenly grasp the solution by perceiving the problem as a whole, rather than through trial and error.
- Holistic Approach: Wertheimer emphasized that effective problem-solving requires seeing the problem in its entirety, integrating various elements into a cohesive understanding, rather than focusing on isolated parts.
- Educational Implications: Productive Thinking has influenced educational approaches, promoting methods that encourage students to engage in insightful and holistic problem-solving.
Image Source: able.ac
Psychologists Influenced by Wertheimer

- Wolfgang Köhler – Köhler’s work on insight learning in chimpanzees and his contributions to Gestalt psychology were heavily influenced by Wertheimer’s theories (Köhler, 1925).
- Kurt Koffka – A founding figure in Gestalt psychology, Koffka extended Wertheimer’s principles to developmental psychology and perception (Koffka, 1935).
- Rudolf Arnheim – Arnheim’s work on art and visual perception drew extensively on Gestalt principles to explain the aesthetics of perception (Arnheim, 1954).
- Solomon Asch – Known for his conformity experiments, Asch was influenced by Gestalt principles in understanding social behavior and perception (Asch, 1956).
- Hans Wallach – Wallach’s research on perception and auditory processing built on Wertheimer’s Gestalt theories, contributing to our understanding of sensory processes (Wallach, 1949).
Impact on Psychology
- Influence on Modern Thought: Max Wertheimer’s ideas have had a profound impact on various fields within psychology, including cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, and educational psychology. His theories on Gestalt principles have transformed our understanding of how we perceive and organize visual information, emphasizing the holistic nature of perception. Wertheimer’s work has also influenced research methodologies, promoting the use of experimental studies to explore cognitive processes.
- Contributions to Related Fields: Wertheimer’s interdisciplinary approach extended his influence to areas such as education, design, and art. His principles of perceptual organization have informed educational practices, leading to the development of teaching methods that emphasize holistic learning and problem-solving. In design, Wertheimer’s theories have been applied to create more effective visual displays and user interfaces, enhancing the usability and aesthetic appeal of various products. In art, Gestalt principles have been used to analyze and understand the perception of visual artworks.
Legacy and Influence
Long-Term Impact
Max Wertheimer’s legacy endures through his lasting contributions to psychology and related fields. His pioneering work in Gestalt psychology has laid the foundation for numerous subsequent theories and research in cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, and educational psychology. Wertheimer’s emphasis on holistic perception and the principles of perceptual organization continues to influence contemporary research and practice in these fields.
Recognition and Honors
Wertheimer received numerous accolades and recognition for his work during his lifetime and posthumously. He was a founding member of the Berlin School of Experimental Psychology and served as a professor at several prestigious universities, including the University of Frankfurt and the New School for Social Research in New York. His contributions to psychology and education have been commemorated through various institutions and awards, underscoring his significant impact on these fields.
Criticism and Controversies
While Max Wertheimer has garnered significant recognition for his contributions to psychology, his work has not been without criticism. Some argue that Gestalt principles lack empirical rigor and are difficult to quantify, posing challenges for experimental validation. Additionally, critics point out that Wertheimer’s focus on perceptual organization may overlook the complexity and variability of individual cognitive processes. Despite these criticisms, Wertheimer’s pioneering research on Gestalt psychology remains a cornerstone of cognitive psychology.
Conclusion
Max Wertheimer’s life and work have profoundly shaped the fields of psychology and education. His theories on Gestalt psychology, the phi phenomenon, and principles of perceptual organization offer valuable insights into human perception and cognitive processes. By emphasizing the holistic nature of perception and the importance of perceptual organization, Wertheimer has provided a comprehensive framework for understanding and enhancing cognitive development and problem-solving. As his legacy continues to unfold, Wertheimer’s contributions to psychology and education will likely inspire future generations of researchers, educators, and practitioners.
Bibliography
- [1] Arnheim, R. (1954). Art and Visual Perception: A Psychology of the Creative Eye. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- [2] Bandura, A. (1986). Social Foundations of Thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- [3] Bruner, J. (1966). Toward a Theory of Instruction. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- [4] Gardner, H. (1983). Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences. New York: Basic Books.
- [5] Koffka, K. (1935). Principles of Gestalt Psychology. New York: Harcourt, Brace.
- [6] Köhler, W. (1925). The Mentality of Apes. London: Kegan Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co.
- [7] Piaget, J. (1926). The Language and Thought of the Child. New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company.
- [8] Piaget, J. (1929). The Child’s Conception of the World. New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company.
- [9] Piaget, J. (1951). Play, Dreams and Imitation in Childhood. New York: W. W. Norton & Company.
- [10] Piaget, J. (1952). The Child’s Conception of Number. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- [11] Piaget, J. (1952). The Origins of Intelligence in Children. New York: International Universities Press.
- [12] Piaget, J. (1955). The Construction of Reality in the Child. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.






