Contents
Introduction

Gestalt Therapy: Techniques, Applications, and Effectiveness
Gestalt Therapy is an experiential form of psychotherapy that focuses on helping individuals become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in the present moment. It emphasizes understanding and integrating various aspects of oneself to achieve personal growth and improved emotional functioning. By using techniques such as role-playing, guided fantasy, and the “empty chair” method, Gestalt Therapy aims to address unresolved issues and enhance self-awareness. This approach is designed to help clients live more fully and authentically by exploring their current experiences and relationships.
This article provides an overview of Gestalt Therapy, including its core principles, unique techniques, and applications in treating various mental health conditions. We will also explore the criticisms and limitations of this approach and its relevance and effectiveness as a therapeutic option today.
What is Gestalt Therapy?
Gestalt Therapy is a humanistic approach to psychotherapy that emphasizes the importance of awareness, presence, and personal responsibility. It was developed by Fritz Perls, Laura Perls, and Paul Goodman and is based on the idea that individuals often experience psychological distress due to unresolved issues and unfulfilled needs from the past. The therapy aims to help clients become more aware of their current experiences, including their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, and to integrate these experiences into a coherent sense of self. Gestalt Therapy often uses experiential exercises and techniques to facilitate this process.
Why Gestalt Therapy is Important?
Gestalt Therapy is important because it provides a holistic approach to understanding and addressing psychological issues. By focusing on present experiences and the therapeutic relationship, Gestalt Therapy helps clients gain insight into their current behavior and emotional state. It encourages individuals to become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and actions, fostering personal growth and self-acceptance. The therapy’s emphasis on the here-and-now and its use of experiential techniques make it a powerful tool for resolving conflicts and enhancing overall well-being.
Understanding How Gestalt Therapy Works
Gestalt Therapy works by helping clients gain awareness of their present experiences and integrate these experiences into a coherent sense of self. The therapy emphasizes the importance of focusing on the here-and-now, exploring unresolved issues and conflicting emotions, and taking responsibility for one’s actions and feelings. Through experiential exercises and techniques, clients develop greater self-awareness, insight, and personal growth. The therapeutic relationship plays a crucial role in facilitating this process, as it provides a supportive and non-judgmental space for exploration and healing.
We will approach Gestalt Therapy in phases: initially covering its essential principles, followed by an exploration of its main therapeutic techniques, and concluding with an examination of its relevance to various psychological conditions.
Simple Overview
Gestalt Therapy is centered on the principle of increasing awareness of the present moment and addressing how past experiences impact current behavior and emotions. It aims to help individuals become more aware of their immediate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. By focusing on the here-and-now, Gestalt Therapy seeks to integrate fragmented or disowned parts of the self
Real-Life Example: A client struggling with unresolved anger towards a parent might use Gestalt Therapy to explore and express these feelings through techniques like the Empty Chair Exercise, leading to greater insight and emotional resolution.
Critical Concepts
- Here-and-Now Awareness: Gestalt Therapy emphasizes the importance of focusing on the present moment and becoming aware of current thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This helps clients understand how their present experiences are influenced by past events.
- Empty Chair Technique: This experiential technique involves having clients engage in a role-play exercise with an empty chair, representing another person or a part of themselves. This allows clients to express and resolve unresolved feelings and conflicts. . This technique helps in processing emotions and gaining insight into their relationships and internal struggles.
- Gestalt Experiments: These are structured activities designed to help clients explore and understand their feelings and behaviors in the present moment. Experiments can include role-playing, visualization, and other experiential exercises. The purpose is to bring hidden feelings and patterns to the surface, allowing clients to experience and process them directly. By engaging in these experiments, clients can gain new perspectives and insights into their personal issues.
- Integration of the Self: The goal of integrating fragmented parts of the self and resolving internal conflicts to achieve a more coherent and authentic sense of self. Achieving this integration leads to a more coherent and authentic sense of self, allowing clients to live more fully and genuinely in alignment with their true selves.
Detailed Assessment
Gestalt Therapy incorporates cognitive, emotional, and experiential elements to provide a comprehensive approach to psychological issues.
- Cognitive Foundations: Gestalt Therapy focuses on how past experiences influence current thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It helps clients understand how their perceptions of the present are shaped by unresolved issues from the past. Instead of directly changing thoughts, it emphasizes becoming aware of these thoughts and how they connect to current feelings and actions.
- Experiential and Emotional Processing: The therapy encourages clients to explore and express emotions in the present moment. Techniques like the Empty Chair Exercise are used to help clients engage with their feelings, confront unresolved emotions, and gain a deeper understanding of themselves. This process allows clients to experience and release emotions they may have been avoiding, leading to emotional integration and healing.
- Insight Development : Gestalt Therapy promotes self-awareness and insight through direct experience and the therapeutic relationship. Clients gain understanding by actively engaging in exercises that help them see their patterns and behaviors more clearly. This awareness supports personal growth and helps resolve inner conflicts, allowing clients to live more authentically and in tune with their true selves.
Difference between Gestalt Theory and Therapy
| Aspect | Gestalt Theory | Gestalt Therapy |
| Definition | A theoretical framework focusing on perception and cognition, emphasizing the whole rather than the sum of parts. | A therapeutic approach based on Gestalt Theory, aimed at increasing self-awareness and integrating fragmented parts of the self. |
| Focus | How people perceive, organize, and make sense of their experiences. | Helping individuals become aware of their present experiences and resolving internal conflicts. |
| Key Concepts | Figure-Ground: How we focus on certain aspects of a scene while other aspects recede into the background. Closure: The tendency to fill in gaps to create a complete picture. | Here-and-Now Awareness: Emphasizing the present moment.- Empty Chair Technique: A tool for role-playing and resolving conflicts.- Gestalt Experiments: Structured activities to explore feelings and behaviors. |
| Application | Applied in understanding cognitive processes, perception, and how we organize our experiences. | Applied in psychotherapy to address emotional and psychological issues through experiential techniques. |
| Purpose | To understand cognitive processes and how we perceive and interpret the world. | To facilitate personal growth, emotional resolution, and integration of fragmented parts of the self. |
| Outcome | Provides insight into how people think and perceive their environment. | Aims to enhance self-awareness, resolve emotional conflicts, and achieve a coherent sense of self. |
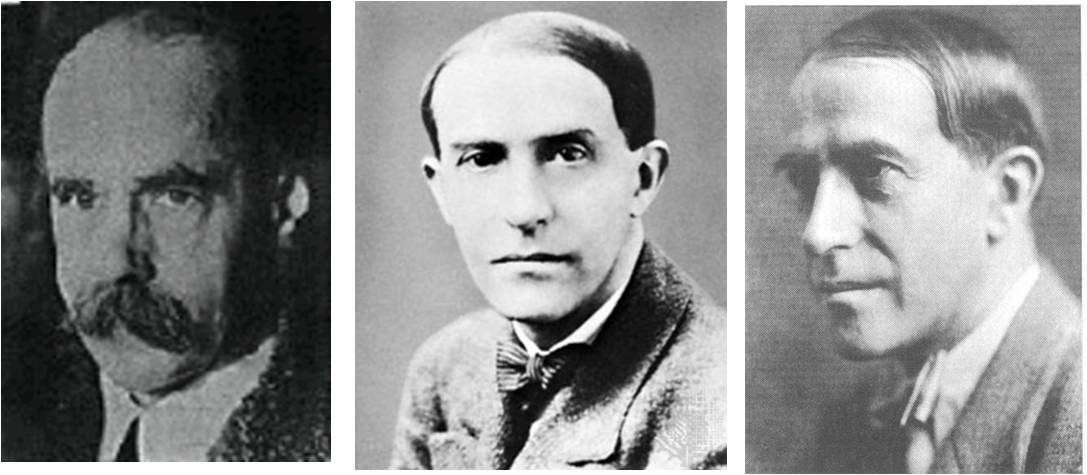

Notable Figures in Gestalt Therapy
- Fritz Perls: The Co-founder of Gestalt Therapy, known for his development of the therapy’s theoretical framework and experiential techniques. Fritz Perls is particularly known for his innovative techniques, such as the Empty Chair Exercise, which help clients explore and resolve internal conflicts.
- Laura Perls: Co-founder of Gestalt Therapy and Fritz Perls’ wife, who contributed to the development of the therapy’s principles and practices. Her work emphasized the importance of the therapeutic relationship and the need for therapists to be fully present and authentic.
- Paul Goodman: Co-founder of Gestalt Therapy, who collaborated with Fritz and Laura Perls on the development of the therapy’s theoretical foundations and techniques. Goodman contributed to the theoretical underpinnings of Gestalt Therapy, particularly in terms of understanding human experience and social context.
Explore the contributions of leading psychologists in our blog.
Applications of Gestalt Therapy in Treating Mental Health Disorders
Depression
Gestalt Therapy can be effective in treating depression by helping clients become more aware of their present experiences and unresolved issues. The therapy’s focus on the here-and-now and its experiential techniques can facilitate emotional processing and self-acceptance.
Example: A client experiencing depression might use Gestalt Therapy to explore and express feelings of sadness and hopelessness through techniques like the Empty Chair Exercise, leading to greater insight and emotional relief.
Image Source: health.com

Anxiety Disorders
Gestalt Therapy helps individuals with anxiety disorders by focusing on present-moment experiences and unresolved fears. The therapy’s emphasis on awareness and personal responsibility can help clients develop coping strategies and reduce anxiety.
Example: A person with generalized anxiety disorder might use Gestalt Therapy to explore and address underlying fears and anxieties through experiential exercises, leading to improved emotional regulation and reduced anxiety.
Image Source: everydayhealth.com

Personality Disorders
Gestalt Therapy can be beneficial for individuals with personality disorders by helping them gain insight into their behavior and emotional patterns. The therapy’s focus on integration and self-awareness can facilitate personal growth and improve interpersonal relationships.
Example: For someone with Borderline Personality Disorder, Gestalt Therapy might focus on exploring conflicting emotions and self-perceptions through techniques like dialogues and body awareness, leading to increased self-understanding and emotional stability.
Image Source: www.rn.com

Relationship Issues
Gestalt Therapy is effective in addressing relationship issues by helping clients explore and resolve unresolved conflicts and communication patterns. The therapy’s emphasis on the here-and-now and experiential techniques can enhance interpersonal dynamics and relationship satisfaction.
Example: A couple experiencing communication problems might use Gestalt Therapy to explore their interactions and emotions through role-playing and dialogues, leading to improved understanding and connection.
Image Source: clintonpower.com.au
Common Myths About Gestalt Therapy
| Myth | Reality |
| Gestalt Therapy is just about emotional expression without structure. | While Gestalt Therapy does place a strong emphasis on exploring and expressing emotions, it is not without structure. The therapy incorporates a range of structured techniques and exercises designed to enhance awareness, facilitate personal growth, and address psychological issues in a focused manner. |
| Gestalt Therapy is only for people with severe psychological issues. | Gestalt Therapy is effective for a diverse range of issues, not just severe psychological problems. It is used for personal growth, improving self-awareness, resolving relationship conflicts, and addressing everyday challenges. The therapy offers a holistic approach that can benefit individuals seeking to understand themselves better and enhance their overall well-being, regardless of the severity of their issues. |
| Gestalt Therapy is too confrontational and aggressive. | Although Gestalt Therapy may involve elements of confrontation, this is done in a way that is supportive and respectful. The goal of confrontation in Gestalt Therapy is to help clients gain insight and self-awareness, not to intimidate or provoke. |
| Gestalt Therapy ignores cognitive factors and focuses solely on emotions. | Gestalt Therapy does not disregard cognitive factors; rather, it integrates cognitive, emotional, and experiential elements to address psychological issues comprehensively. While it emphasizes the importance of emotional awareness and experience, it also considers how cognitive processes influence behavior and perception. |
Criticisms and Limitations
- Lack of Empirical Evidence: Gestalt Therapy has been criticized for its limited empirical support compared to more research-backed approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Despite this, growing evidence suggests its effectiveness in various contexts, particularly in enhancing self-awareness and resolving present-moment issues.
- Intensity of Experiential Techniques: The therapy’s use of intense experiential techniques, such as role-playing and confrontation, may not be suitable for all clients. These techniques can be challenging and emotionally demanding, potentially leading to discomfort or resistance in some individuals.
- Focus on Present-Moment Experiences: Gestalt Therapy emphasizes the here-and-now, which may sometimes overlook the importance of exploring past experiences and historical factors that contribute to psychological issues. This focus on present-moment experiences might limit the exploration of underlying causes of current difficulties.
Conclusion
Gestalt Therapy offers a dynamic approach to psychotherapy by focusing on awareness, present-moment experiences, and personal responsibility. Through experiential techniques and a strong emphasis on the therapeutic relationship, Gestalt Therapy helps clients gain insight into their behavior and emotions, facilitating personal growth and resolution of psychological conflicts. Despite some criticisms related to empirical support and intensity, Gestalt Therapy remains a relevant and effective option for individuals seeking to enhance self-awareness and improve their overall well-being.
References
- Perls, F., Hefferline, R. F., & Goodman, P. (1951). Gestalt therapy: Excitement and growth in the human personality. Julian Press.
- Perls, F., & Perls, L. (1973). Gestalt therapy verbal expressions. Random House.
- Goodman, P. (1961). Gestalt therapy: Excitement and growth in the human personality. Julian Press.
- Yontef, G. M. (1993). Awareness, dialogue, and process: Essays on Gestalt therapy. Gestalt Journal Press.
- Nevis, E. C. (1992). Organizational Consulting: A Gestalt Approach. Guilford Press.
- Clarkson, P. (1999). The therapeutic relationship in Gestalt therapy. Routledge.
- Schwartz, R. (1995). Gestalt therapy: History, theory, and practice. Sage Publications.
- Joyce, P., & Sills, C. (2010). Skills in Gestalt Counselling & Psychotherapy. Sage Publications.
- Zinker, J. (1978). Creative process in Gestalt therapy. Harper & Row.
- Melnick, J. (1987). Gestalt therapy in action. Jossey-Bass.
- Schneider, J., & Kratochwill, T. R. (2012). Gestalt therapy: A guide to contemporary practice. Routledge.
- Perls, F. (1992). In and out of the garbage can: An approach to Gestalt therapy. Science and Behavior Books.
Explore more Theories & Therapies








