Contents
Introduction
David Eagleman is a prominent American neuroscientist, author, and television host renowned for his groundbreaking research on brain plasticity, sensory substitution, time perception, and synesthesia. As a leading figure in cognitive neuroscience, Eagleman has significantly advanced our understanding of how the brain processes information, adapts to new experiences, and constructs reality. His innovative approaches to studying the brain have not only influenced academic research but also inspired public interest in neuroscience through his engaging books, TED Talks, and television series such as The Brain with David Eagleman. Eagleman’s work bridges the gap between complex scientific concepts and everyday experiences, making neuroscience accessible and captivating to a broad audience.

This article explores Eagleman’s life, major theories, and the profound impact of his work on modern psychology, neuroscience, and public perception of the brain.
Early Life and Education
David Eagleman was born on April 25, 1971, in Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA. From an early age, Eagleman exhibited a keen interest in understanding how the brain works, fueled by his curiosity about perception and cognition. His formative years were marked by a fascination with science and the mysteries of the human mind, setting the stage for his future academic and research endeavors. Eagleman’s commitment to unraveling the complexities of the brain led him to pursue advanced studies in neuroscience, where he would make significant contributions to the field.
Image Source: The Lavin Agency

Educational Journey
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Undergraduate Education | Eagleman earned his Bachelor of Arts degree in Psychology from Baylor University in 1993. During his undergraduate studies, he developed a strong foundation in cognitive psychology and neuroscience, which sparked his enduring interest in brain function and perception. |
| Graduate Studies | He pursued his Ph.D. in Neuroscience at Baylor University, completing his dissertation on the neural mechanisms of sensory substitution in 1996. His doctoral research focused on how the brain adapts to new sensory inputs, laying the groundwork for his future studies on brain plasticity and perception. |
| Postdoctoral Training | After earning his doctorate, Eagleman conducted postdoctoral research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) under the mentorship of renowned neuroscientist Eric Kandel. His postdoctoral work further deepened his expertise in neuroplasticity and the brain’s ability to reorganize itself in response to new experiences. |
| Academic Positions | Eagleman holds the position of New Century Chair in Neuroscience and is the founder and director of the Studio for Creative Intelligence at Stanford University. His role as a professor allows him to mentor the next generation of neuroscientists and engage in cutting-edge research on brain function and cognition. |
Influences and Early Career
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Eric Kandel | Eagleman was profoundly influenced by Eric Kandel’s work on the biological mechanisms of learning and memory. Kandel’s research provided a foundational understanding of how neural circuits adapt, which inspired Eagleman’s own studies on brain plasticity and sensory substitution. |
| Neuroplasticity Research | Early in his career, Eagleman was influenced by pioneering research on neuroplasticity, which examines the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This concept became a central theme in his work, particularly in understanding how the brain adapts to sensory loss and new experiences. |
| Cognitive Psychology | Eagleman’s background in cognitive psychology shaped his approach to studying perception and consciousness. The integration of cognitive theories with neuroscience allowed him to explore how mental processes are grounded in neural activity. |
| Technological Innovation | Inspired by advancements in technology, Eagleman has leveraged innovative tools and methods, such as virtual reality and neuroimaging, to study the brain’s response to novel sensory inputs and to develop practical applications for sensory substitution and augmentation. |
| Public Engagement | Recognizing the importance of communicating scientific ideas to the public, Eagleman was influenced by science communicators and educators who demonstrated the value of making complex concepts accessible. This influence led him to pursue writing and media projects that bridge the gap between neuroscience and everyday life. |
Major Theories and Work
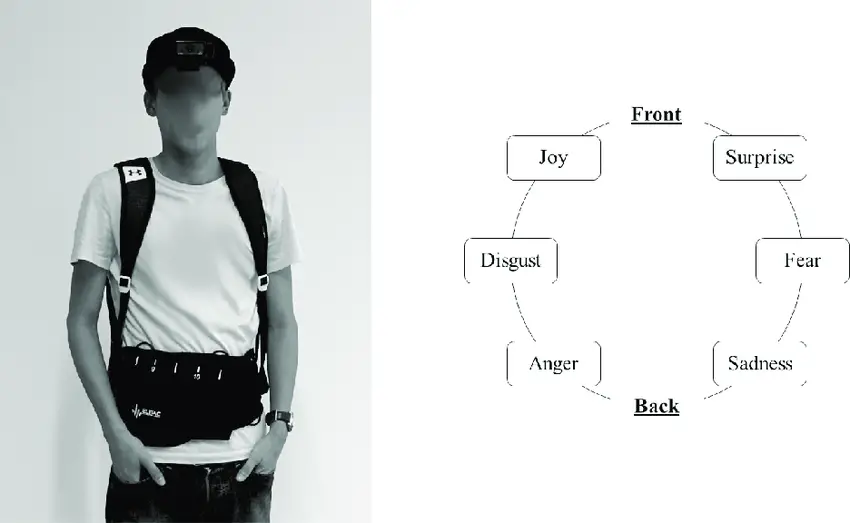
Brain Plasticity and Sensory Substitution
David Eagleman’s research on brain plasticity and sensory substitution has significantly advanced our understanding of how the brain adapts to new sensory inputs and recovers from sensory loss. Key elements of this theory include:
- Sensory Substitution Devices: Eagleman developed innovative devices that translate visual information into tactile or auditory signals, allowing individuals with visual impairments to perceive their environment through alternative senses.
- Neuroplasticity: Eagleman’s studies emphasize the brain’s capacity for plasticity—the ability to change and adapt in response to new experiences. His research shows that even in adulthood, the brain can form new neural connections, enhancing cognitive functions and compensating for sensory deficits.
- Adaptive Learning: Eagleman explores how adaptive learning processes enable individuals to acquire new skills and adapt to changing environments. His work highlights the interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental influences in shaping brain development and function.
Image Source: ResearchGate
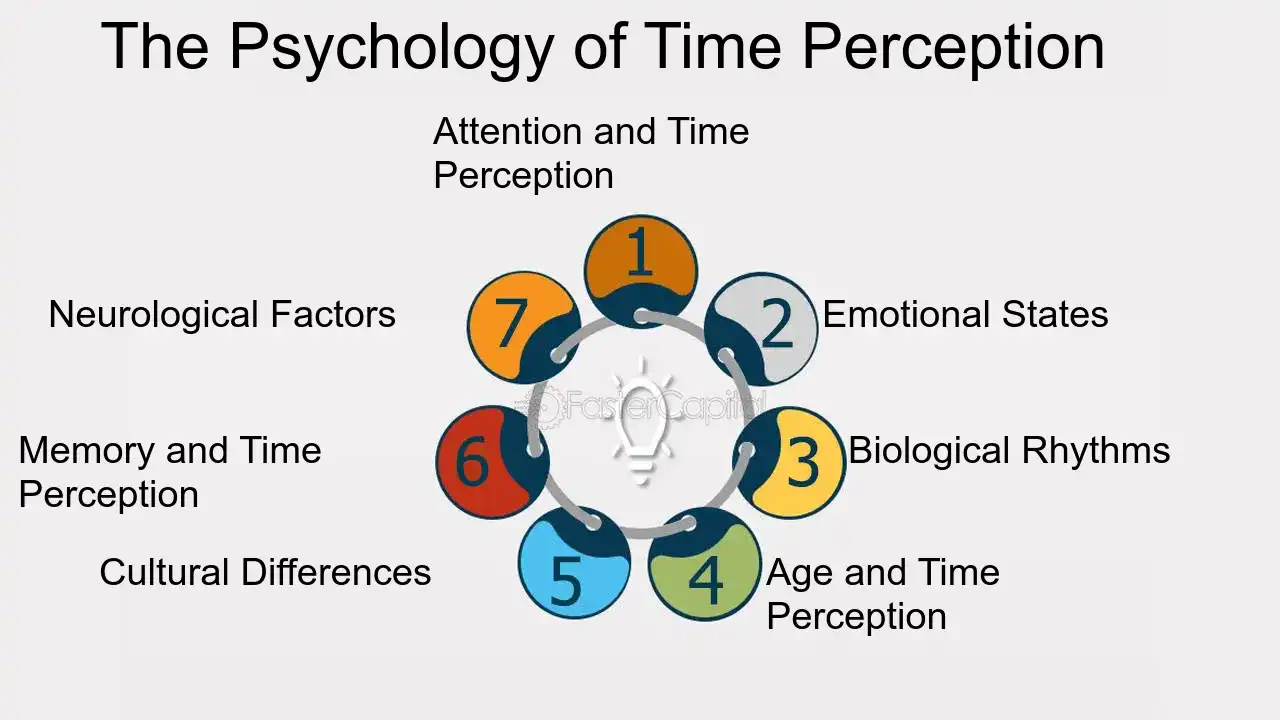
Time Perception
Eagleman has made significant contributions to understanding how the brain perceives time, investigating the neural mechanisms that underlie our subjective experience of time. Key aspects include:
- Temporal Illusions: Eagleman studies various temporal illusions that reveal the brain’s role in constructing the perception of time. His research explores how the brain integrates sensory information and anticipates future events to create a coherent temporal experience.
- Neural Correlates of Time: He investigates the specific neural circuits and processes involved in time perception, identifying brain regions that contribute to the estimation and tracking of time intervals.
- Applications in Technology: Eagleman applies his insights into time perception to develop technologies that manipulate temporal experience, such as virtual reality environments that alter users’ sense of time passage.
Image Source: FasterCapital
Famous Books and Publications

Incognito: The Secret Lives of the Brain

The Brain: The Story of You

Livewired: The Inside Story of the Ever-Changing Brain

The Safety Net: Surviving Pandemics and Other Disasters
Influence on Contemporary and Future Psychological Research
David Eagleman’s theories continue to shape contemporary psychological research, inspiring new studies and applications across various domains:
- Advancements in Neuroplasticity: Eagleman’s research on brain plasticity has sparked numerous studies exploring how the brain adapts to new sensory inputs and recovers from injury. His work has led to the development of therapies and technologies designed to leverage neuroplasticity for cognitive enhancement and rehabilitation, advancing treatment options for brain injury and neurological disorders.
- Sensory Substitution and Augmentation: Building on his work in sensory substitution, Eagleman’s research has influenced the creation of assistive devices for sensory impairments, such as those that convert sound into tactile stimuli. Future research will likely focus on more advanced forms of sensory augmentation, aiming to expand human perception and interaction with the environment.
- Time Perception Studies: Eagleman’s insights into time perception have inspired further exploration of the neural and cognitive processes governing our sense of time. This research has important implications for understanding disorders like ADHD and schizophrenia, which involve time perception abnormalities, and for developing therapies to improve temporal awareness.
- Multisensory Integration: Eagleman’s work on synesthesia and multisensory integration has advanced research into how the brain processes and merges information from different senses. This research is vital for improving sensory substitution devices and enhancing human-computer interactions, with applications in both assistive technology and virtual reality.
- Public Engagement and Science Communication: Eagleman’s success in making neuroscience accessible to the public has set a new standard for science communication. His work has influenced how researchers engage with broader audiences, encouraging the development of strategies that make complex scientific ideas more relatable and engaging for non-specialists.
Psychologists and Neuroscientists Influenced by David Eagleman

- Anil Seth: A neuroscientist known for his work on consciousness and perception, Seth has been influenced by Eagleman’s research on how the brain constructs reality and the nature of conscious experience.
- V.S. Ramachandran: Renowned for his work on phantom limbs and neuroplasticity, Ramachandran’s research parallels Eagleman’s studies on sensory substitution and brain adaptability, fostering mutual inspiration and collaboration in understanding brain function.
- Tali Sharot: A cognitive neuroscientist specializing in decision-making and optimism bias, Sharot has drawn on Eagleman’s insights into unconscious processes and brain plasticity to inform her own research on how expectations shape human behavior.
- Joseph LeDoux: Known for his research on the neural mechanisms of emotion, particularly fear, LeDoux has been influenced by Eagleman’s exploration of how the brain processes sensory information and constructs emotional experiences.
Impact on Neuroscience
- Influence on Modern Thought: David Eagleman’s groundbreaking research in neuroscience has reshaped the understanding of brain function, consciousness, and human perception. By exploring the brain’s plasticity and the nature of time perception, Eagleman bridges the gap between cognitive science and real-world applications in technology and therapy. His work has inspired interdisciplinary approaches that combine neuroscience, psychology, and artificial intelligence, fostering deeper insights into human cognition and behavior.
- Legacy and Recognition: Eagleman has earned numerous accolades, including the prestigious MacArthur Fellowship for his innovative contributions to neuroscience. Recognized as one of Time Magazine’s 100 Most Influential People, his role as a leading science communicator is cemented by his acclaimed PBS series The Brain with David Eagleman. He has also received academic honors from prominent scientific organizations, further highlighting his impact on cognitive neuroscience. Eagleman’s ability to communicate complex scientific ideas has solidified his legacy, with his theories widely adopted in academic curricula, research, and applied settings.
Conclusion
David Eagleman’s pioneering work in neuroscience has had a profound and lasting impact on the understanding of brain plasticity, sensory substitution, and time perception. By elucidating the brain’s capacity to adapt and construct reality from diverse sensory inputs, Eagleman has provided invaluable insights into the dynamic nature of neural processes and human cognition. His innovative research, engaging writings, and effective science communication have not only advanced academic knowledge but also inspired public interest in the complexities of the human brain. Eagleman’s enduring legacy continues to influence both scientific research and the broader public’s appreciation of neuroscience, making him a pivotal figure in contemporary psychology and cognitive science.
Bibliography
- Eagleman, D. (2009). Sum: Forty Tales from the Afterlives. William Morrow.
- Eagleman, D. (2011). Incognito: The Secret Lives of the Brain. Pantheon.
- Eagleman, D. (2015). The Brain: The Story of You. Pantheon Books.
- Eagleman, D. (2015). The Brain’s Way of Healing: Remarkable Discoveries and Recoveries from the Frontiers of Neuroplasticity. Viking.
- Eagleman, D. (2020). Livewired: The Inside Story of the Ever-Changing Brain. Pantheon Books.
- Eagleman, D. (2007). “Sensory Substitution and the Brain.” Scientific American, April 2007.
- Eagleman, D. (2012). “The Neuroscience of Time.” TED Talk. Retrieved from https://www.ted.com/talks/david_eagleman_the_neuroscience_of_time.
- Eagleman, D. (2014). “How Your Brain Constructs Reality.” Nature Neuroscience, 17(3), 245–248.
- Eagleman, D. (2017). “The Plasticity of the Brain.” Harvard Business Review, July-August 2017.
- Eagleman, D. (2019). “The Future of the Brain.” Scientific American, January 2019.
