Contents
Introduction
Daniel Goleman is an influential psychologist, science journalist, and author known for his groundbreaking work on emotional intelligence. Goleman’s research has significantly advanced our understanding of how emotional and social competencies influence personal and professional success. His contributions have had a profound impact on psychology, education, and organizational behavior, bringing the concept of emotional intelligence to the forefront of discussions about human potential and leadership.

In this article, we will explore Daniel Goleman’s groundbreaking research on emotional intelligence, examining how his work has advanced our understanding of emotional and social competencies and their influence on personal and professional success, and its impact on psychology, education, and organizational behavior.
Early Life and Education
Daniel Goleman was born on March 7, 1946, in Stockton, California. He grew up in a family that valued intellectual pursuits; his mother was a teacher, and his father was a humanities professor. This nurturing environment fostered his early interest in understanding human behavior and the mind. Goleman’s curiosity about the inner workings of people’s emotions and social interactions was evident from a young age, setting the stage for his future academic and professional journey.

Educational Journey
| Aspect | Details |
| Early Education | Goleman attended local schools in Stockton, where he developed a strong foundation in the humanities and social sciences. |
| Amherst College | Goleman earned his Bachelor of Arts degree in Psychology in 1967. |
| Harvard University | Goleman pursued his Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology and Personality Development under the supervision of David C. McClelland, completing his dissertation on meditation and altered states of consciousness in 1974. |
| Academic Career | After completing his doctorate, Goleman held academic positions and worked as a science journalist for The New York Times, where he reported on brain and behavioral sciences. He later became a full-time author and consultant, focusing on emotional intelligence and leadership development. |
Timeline of Early Influences
| Aspect | Details |
| David C. McClelland | McClelland’s work on motivation and competency influenced Goleman’s understanding of the role of emotional competencies in personal and professional success. |
| Richard J. Davidson | Davidson’s research on the neural bases of emotion and meditation influenced Goleman’s interest in the biological underpinnings of emotional intelligence. |
| Paul Ekman | Ekman’s work on facial expressions and emotions provided a foundation for Goleman’s exploration of emotional recognition and regulation. |
| Herbert Benson | Benson’s research on the relaxation response and meditation shaped Goleman’s early work on the psychological and physiological effects of mindfulness. |
Major Theories and Works

Emotional Intelligence
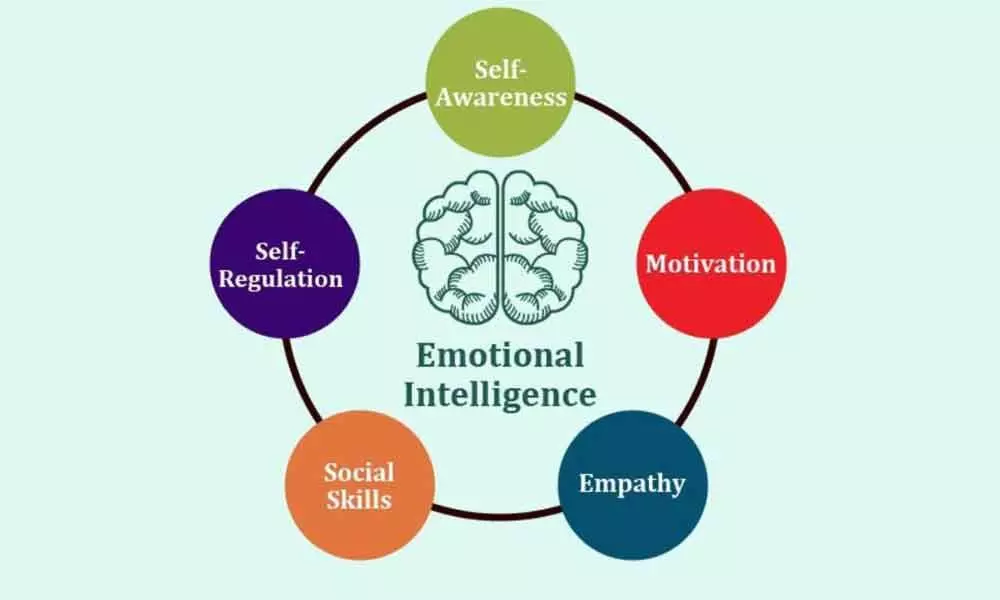
Daniel Goleman is best known for his work on emotional intelligence, a concept that he popularized with his 1995 book Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. Emotional intelligence (EI) refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the ability to recognize, understand, and influence the emotions of others. Goleman identifies five key components of EI:
- Self-awareness: The ability to recognize and understand one’s own emotions.
- Self-regulation: The ability to manage one’s emotions and impulses.
- Motivation: The drive to achieve goals for intrinsic reasons.
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others.
- Social skills: The ability to manage relationships and build networks.
Image Source: teammedglobal.com
Leadership and Emotional Intelligence
In his book Primal Leadership: Realizing the Power of Emotional Intelligence, co-authored with Richard Boyatzis and Annie McKee, Goleman explores the role of emotional intelligence in effective leadership. Goleman identifies six leadership styles based on different components of emotional intelligence:
- Visionary: Inspires and motivates by providing a clear vision of the future.
- Coaching: Develops people for the future by focusing on their personal strengths and growth.
- Affiliative: Creates harmony and builds emotional bonds within the team.
- Democratic: Forges consensus through participation and collaboration.
- Pacesetting: Sets high standards for performance and leads by example.
- Commanding: Provides clear direction and expects compliance, effective in crisis situations.
Image Source: linkedin.com

Focus and Attention
In his book Focus: The Hidden Driver of Excellence, Goleman explores the role of attention in achieving excellence. He argues that focus is a critical component of emotional intelligence and is essential for success in various domains. Goleman identifies three types of focus:
- Inner focus: Self-awareness and self-management.
- Other focus: Empathy and relationship management.
- Outer focus: Understanding the larger context and environment.
Goleman’s work on focus highlights the importance of attention in navigating the complexities of modern life and achieving high performance.
Image Source: inc.com

Social and Emotional Learning (SEL)
Daniel Goleman has been a leading advocate for integrating social and emotional learning (SEL) into educational systems. Key elements include:
- Impact on Academic and Life Success: Goleman’s advocacy has shown that integrating SEL into education not only improves academic performance but also equips students with the emotional and social tools necessary for navigating life’s challenges.
- Emotional Intelligence: SEL programs aim to enhance students’ emotional intelligence, which involves understanding and managing one’s own emotions and recognizing and influencing the emotions of others.
- Skill Development: SEL teaches critical life skills, including self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and effective communication, which are essential for personal and professional success.
Image Source: vietnamteachingjobs.com
Psychologists Influenced by Goleman

- Richard Boyatzis – Boyatzis’s work on leadership and emotional intelligence has been heavily influenced by his collaborations with Goleman (Boyatzis, 2006).
- Annie McKee – McKee’s research on leadership and organizational behavior draws from Goleman’s theories on emotional intelligence (McKee, 2005).
- Marc Brackett – Brackett’s work on social and emotional learning (SEL) has been shaped by Goleman’s advocacy for incorporating SEL into educational curricula (Brackett, 2019).
- Paul Ekman – Ekman’s research on emotions and facial expressions aligns with Goleman’s exploration of emotional recognition and regulation (Ekman, 2003).
- Richard Davidson – Davidson’s studies on the neural bases of emotion and well-being have been influenced by Goleman’s interest in the biological underpinnings of emotional intelligence (Davidson, 2012)
Impact on Psychology
Influence on Modern Thought
Daniel Goleman’s ideas have had a profound impact on various fields within psychology, education, and organizational behavior. His theories on emotional intelligence have transformed our understanding of human competencies, emphasizing the importance of emotional and social skills in achieving personal and professional success. Goleman’s work has also influenced research methodologies, promoting the use of empirical and interdisciplinary approaches to study emotional and social intelligence. His contributions have been instrumental in bridging the gap between psychological science and practical applications in education and organizational settings.
Contributions to Related Fields
Goleman’s interdisciplinary approach has extended his influence to areas such as education, organizational behavior, and public policy. His insights into emotional intelligence have informed educational practices, leading to the development and implementation of social and emotional learning (SEL) programs in schools worldwide. In organizational behavior, Goleman’s work has influenced leadership training and development programs, emphasizing the importance of emotional competencies in effective leadership. His research has also informed public policy initiatives aimed at promoting emotional well-being and mental health.
Legacy and Influence
- Long-Term Impact: Daniel Goleman’s legacy endures through his lasting contributions to psychology, education, and organizational behavior. His pioneering work on emotional intelligence has laid the foundation for numerous subsequent theories and research. Goleman’s emphasis on understanding the emotional and social dimensions of human behavior continues to influence contemporary research and practice. His ability to communicate complex scientific ideas to both academic and public audiences has made him a key figure in promoting emotional literacy and fostering dialogue on critical issues.
- Recognition and Honors: Goleman has received numerous accolades and recognition for his work. He has been a frequent speaker at academic conferences and public forums, and his books have received critical acclaim and widespread readership. Goleman’s contributions to emotional intelligence and education have been acknowledged through various awards and honors, including the American Psychological Association’s Lifetime Achievement Award. His efforts to promote emotional intelligence and social and emotional learning have been widely celebrated.
- Criticism and Controversies: While Daniel Goleman has garnered significant recognition for his contributions to psychology and organizational behavior, his work has not been without criticism. Some argue that the broad concept of emotional intelligence may lack the precision needed for rigorous scientific measurement. Additionally, the popularization of emotional intelligence has sparked debate, with critics suggesting that it may oversimplify the complexities of human behavior and overemphasize the role of emotional competencies in achieving success. Despite these criticisms, Goleman’s commitment to promoting emotional literacy and understanding continues to inspire debate and further investigation in the fields of psychology and beyond.
Conclusion
Daniel Goleman’s life and work have profoundly shaped the fields of psychology, education, and organizational behavior. His theories on emotional intelligence, leadership, and focus offer valuable insights into human behavior and the complexities of emotional and social competencies. By emphasizing the importance of understanding and developing emotional intelligence, Goleman has provided a comprehensive framework for enhancing personal and professional success. As his legacy continues to unfold, Goleman’s contributions to psychology, education, and public engagement will likely inspire future generations of researchers, educators, and practitioners.
Bibliography
- [1] Boyatzis, R. E. (2006). An Integrative Theory of Leadership. In G. R. Goethals & G. J. Sorenson (Eds.), The Quest for a General Theory of Leadership. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing
- [2] Davidson, R. J. (2012). The Emotional Life of Your Brain: How Its Unique Patterns Affect the Way You Think, Feel, and Live—and How You Can Change Them. New York: Hudson Street Press.
- [3] Ekman, P. (2003). Emotions Revealed: Recognizing Faces and Feelings to Improve Communication and Emotional Life. New York: Times Books.
- [4] Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. New York: Bantam Books.
- [5] Goleman, D. (1998). Working with Emotional Intelligence. New York: Bantam Books.
- [6] Goleman, D. (2006). Social Intelligence: The New Science of Human Relationships. New York: Bantam Books.
- [7] Goleman, D. (2013). Focus: The Hidden Driver of Excellence. New York: Harper.
- [8] Goleman, D., Boyatzis, R., & McKee, A. (2002). Primal Leadership: Realizing the Power of Emotional Intelligence. Boston: Harvard Business Review Press.
- [9] McKee, A. (2005). Resonant Leadership: Renewing Yourself and Connecting with Others Through Mindfulness, Hope, and Compassion. Boston: Harvard Business Review Press.






