Contents
Introduction
Albert Ellis was a pioneering psychologist and psychotherapist, best known for developing Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), a cognitive-based therapeutic approach that has profoundly influenced the field of psychology. Ellis’s work revolutionized cognitive therapies by challenging irrational beliefs and promoting emotional well-being through rational thinking. His innovative approaches have had a lasting impact on psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and self-help movements.

This article explores Ellis’s life, major theories, and the profound influence of his work on modern psychology. It explore into how his development of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) revolutionized the understanding and treatment of emotional and behavioral issues.
Early Life and Education
Albert Ellis was born on September 27, 1913, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and grew up in New York City. His interest in psychology emerged early on due to personal struggles with chronic illnesses and family dynamics. These experiences fostered a passion for understanding human emotions and thought patterns. Ellis’s commitment to self-reliance and independence guided his academic pursuits and later contributed to his revolutionary therapeutic approaches.
Image Source: totallyhistory.com

Educational Journey
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Early Education | Ellis showed exceptional academic ability from a young age, excelling in subjects related to philosophy and psychology. His early fascination with rational thinking and logical analysis would later be foundational to his therapeutic approach. |
| Graduate Studies | He earned a Master’s degree from Teachers College, Columbia University, in 1943, followed by a Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology in 1947. Ellis’s research focused on understanding human emotions, rational thought processes, and how these could influence mental health and well-being. |
| Academic Contributions | After completing his studies, Ellis sought to merge his academic background with practical therapeutic methods, setting the groundwork for his development of REBT. He integrated insights from philosophy, particularly Stoicism, into his clinical work, leading to groundbreaking new techniques. |
Influences and Early Career
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Sigmund Freud | Ellis initially trained in psychoanalysis under the influence of Sigmund Freud, but he later became disillusioned with its long and introspective process. This shift in perspective led Ellis to seek more direct and rational therapeutic methods, diverging from psychoanalytic traditions. |
| Alfred Adler | Adler’s emphasis on social influences and personal goals greatly impacted Ellis’s approach to therapy. Ellis incorporated Adler’s ideas about overcoming feelings of inferiority, focusing on empowering individuals to take control of their emotional and behavioral responses. |
| Stoic Philosophy | The Stoic philosophers, particularly Epictetus and Marcus Aurelius, were crucial influences on Ellis’s development of REBT. Their teachings on rationality, emotional regulation, and the importance of perception in human suffering provided the philosophical foundation for his therapeutic model. |
| Behavioral Therapy | Ellis was also influenced by the emerging field of behavior therapy, incorporating principles of reinforcement and behavioral modification into his cognitive framework. This integration of cognitive and behavioral techniques became a hallmark of his Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT). |
Major Theories and Work
Albert Ellis’s REBT is one of the first cognitive-behavioral therapies that emphasize the role of irrational beliefs in emotional distress. Key elements include:
- ABC Model: Ellis developed the ABC model, which explains how Activating events lead to irrational Beliefs, resulting in Consequences like emotional distress.
- Disputation Techniques: A core aspect of REBT involves teaching clients to challenge and dispute irrational beliefs, encouraging rational thinking to improve emotional regulation.
- Applications: REBT has been widely applied in treating various conditions such as anxiety, depression, and anger management, empowering clients to change their thought patterns for better mental health outcomes.
Image Source: alinaphalonen.com
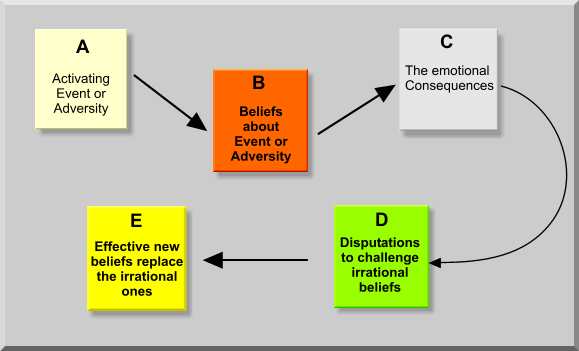
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
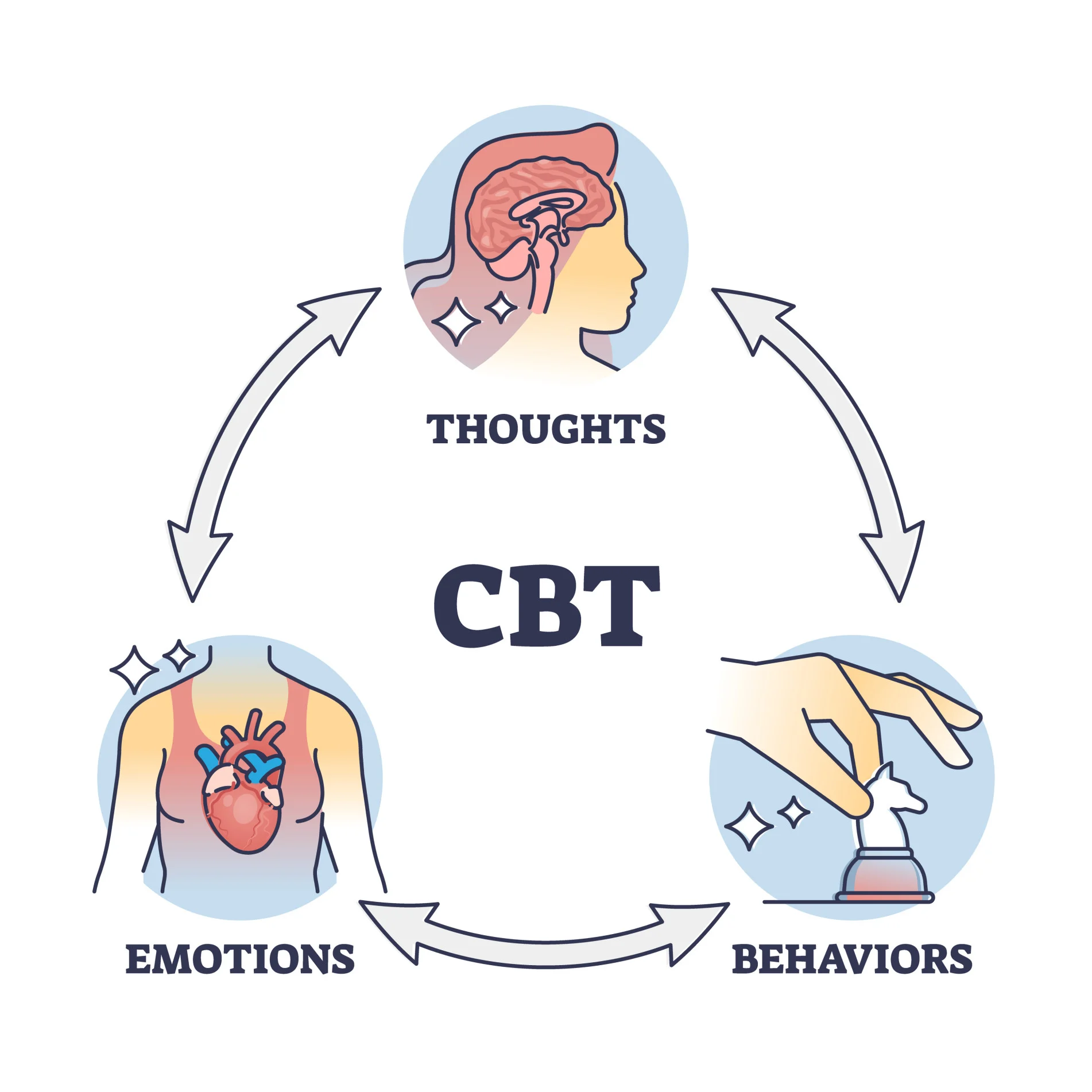
Influence on Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Ellis’s work laid the foundation for Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), influencing future therapeutic models. Key elements include:
- Cognitive Restructuring: Ellis’s concept of changing irrational beliefs set the stage for cognitive restructuring techniques in CBT, which help clients reframe negative thoughts.
- Collaborative Therapeutic Relationship: While Ellis’s approach was more direct, his work influenced the importance of collaboration between therapist and client in modern CBT, fostering a partnership in addressing cognitive distortions.
- Impact: Ellis’s theories are seen in contemporary CBT interventions, shaping how therapists help clients manage anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders through cognitive methods.
Image Source: simplypsychology.org
Ellis’s pioneering work has also fueled the self-help movement, offering individuals practical tools for emotional regulation. Key elements include:
- Promoting Rational Self-Help: Ellis’s books and workshops have encouraged individuals to adopt rational self-help techniques, emphasizing the importance of personal responsibility in mental health.
- Reach: His theories have transcended traditional therapy settings, reaching a global audience through books, workshops, and public talks aimed at empowering individuals to manage their emotions.
- Impact: Ellis’s self-help philosophy continues to inspire a generation of individuals to take charge of their emotional well-being through rational thinking and self-guided therapy.
Image Source: thepositivepsychologypeople.com

Self-Help Movement
Famous Books and Publications

Reason and Emotion in Psychotherapy

A Guide to Rational Living by Ellis’s

Overcoming Destructive Beliefs, Feelings, and Behaviors

The Myth of Self-Esteem by
Ellis’s
Influence on Contemporary and Future Psychological Research
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies (CBT): Ellis’s development of REBT directly influenced the rise of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy, particularly in its emphasis on restructuring irrational thoughts. This foundation remains central to the most widely used therapeutic models today, including Aaron Beck’s Cognitive Therapy.
- Empirical Validation of Psychotherapies: Ellis emphasized the need for empirical evidence to support therapeutic techniques, laying the groundwork for today’s evidence-based practices. Modern psychology continues to prioritize research-driven approaches, with numerous studies validating cognitive restructuring methods.
- Therapist Training and Techniques: His direct, sometimes confrontational style, although controversial, has influenced modern therapist training by demonstrating the importance of therapist-client dynamics. Ellis’s methods have informed debates about how therapeutic interventions should balance directness with empathy.
- Integration of Self-Help with Psychotherapy: Ellis’s work popularized the integration of self-help strategies into clinical practice. His ideas have inspired the development of tools and resources that empower clients to take an active role in managing their mental health, a trend that continues to grow with digital and app-based therapeutic tools.
- Focus on Irrational Beliefs in Research: Ongoing psychological research often explores the impact of irrational beliefs on mental health, a concept introduced by Ellis. His influence is seen in studies examining the relationship between cognition and emotional regulation, continuing to inspire future research in cognitive and emotional interactions.
Psychologists Influenced by Albert Ellis

- Aaron T. Beck: The founder of Cognitive Therapy (CT), Beck’s approach was heavily influenced by Ellis’s focus on cognitive restructuring and the role of irrational beliefs in emotional distress. Beck’s cognitive model became a cornerstone for modern cognitive-behavioral therapies used globally.
- David D. Burns: A prominent psychiatrist and author of Feeling Good, Burns expanded on Ellis’s work by promoting self-help techniques for combating depression and anxiety, rooted in cognitive-behavioral principles. His book became a foundational text in the self-help genre, bringing cognitive restructuring to a wider audience.
- Donald Meichenbaum: Known for his work on Cognitive Behavioral Modification (CBM), Meichenbaum integrated Ellis’s ideas about challenging irrational thoughts to develop therapeutic approaches for various disorders. He introduced stress inoculation training, further blending cognitive and behavioral methods.
- Judith S. Beck: Daughter of Aaron Beck and a leading figure in Cognitive Therapy, she built on Ellis’s framework by focusing on cognitive restructuring as a way to improve emotional and behavioral regulation. Her work continues to shape educational programs in CBT training across the world.
- Michael Neenan: A cognitive-behavioral therapist and author, Neenan adapted Ellis’s REBT to enhance resilience training and improve emotional well-being in clients. His contributions have focused on using REBT principles for personal growth and workplace coaching.
Impact on Psychology
- Influence on Modern Thought: Albert Ellis’s creation of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) brought a new focus to psychotherapy by emphasizing the importance of rational thinking in managing emotions and behaviors. His work shifted the approach to therapy from just understanding feelings to actively changing thought patterns that cause distress. This idea became a foundation for many other therapies, like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and has influenced generations of therapists in helping people deal with emotional challenges.
- Legacy and Recognition: Ellis received many honors for his work in psychology, including the American Psychological Association’s Distinguished Professional Contributions Award. His influence continues today through the widespread use of REBT and its significant impact on the development of cognitive-based therapies. His ideas remain central to how modern therapy helps people manage their thoughts and emotions effectively.
- Criticisms and Controversies: While Ellis’s approach to therapy was highly effective for many, his direct and sometimes confrontational style has been criticized for being too harsh. Some critics feel that his method may not be suitable for everyone, especially clients who need a more compassionate or empathetic approach. Despite these concerns, REBT remains a widely respected therapeutic method.
Conclusion
Albert Ellis’s contributions to psychology, particularly through the development of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, have had a profound and lasting impact on the field. His pioneering work in cognitive-behavioral approaches revolutionized therapeutic practices, offering individuals effective tools for emotional regulation and self-improvement. Ellis’s enduring legacy continues to shape the treatment of psychological disorders, emphasizing the importance of rational thinking in achieving mental health.
Bibliography
- Ellis, A. (1994). Reason and Emotion in Psychotherapy. Birch Lane Press.
- Ellis, A., & Dryden, W. (1997). The Practice of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy. Springer.
- Ellis, A. (2001). Feeling Better, Getting Better, Staying Better. Impact Publishers.
- Ellis, A., & MacLaren, C. (2005). Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: A Therapist’s Guide. New Harbinger.
- Ellis, A. (2004). Overcoming Destructive Beliefs, Feelings, and Behaviors. Prometheus Books.
- Ellis, A., & Harper, R. A. (1975). A New Guide to Rational Living. Wilshire Book Company.
- Ellis, A. (2003). The Road to Tolerance: The Philosophy of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy. Prometheus Books.
- Ellis, A., Bernard, M. E., & Wolfe, J. L. (2007). Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy. Springer.
- Ellis, A., & Blau, S. (1998). How to Keep People from Pushing Your Buttons. Citadel Press.
- Ellis, A., & Grieger, R. (1986). Handbook of Rational-Emotive Therapy: Volume II. Springer.






