Contents
Introduction
Abraham Maslow was an American psychologist who developed a hierarchy of needs to explain human motivation. His theory suggested that people have a number of basic needs that must be met before people move up the hierarchy to pursue more social, emotional, and self-actualizing needs.
In this article, we will explore Abraham Maslow’s theories, his innovative approach to humanistic psychology, and his influence on both psychology and broader fields such as education and business. Explore more psychologists here.

Life Of Abraham Maslow
Abraham Maslow was born on April 1, 1908, in Brooklyn, New York, the first of seven children born to Jewish parents who emigrated from Russia.
He described his early childhood as unhappy and lonely, often spending time in the library immersed in books. Maslow married Bertha Goodman in 1928, and the couple had two daughters, Ellen and Anne.
Bettmann Archive / Getty Images

His relationships with colleagues and students reflected his dedication, intellect, and vision, enriching both his personal and professional life
- Childhood Environment: Growing up in a family that valued education, Maslow developed an early interest in human behavior and psychology.
- Early Career and Influences: Initially trained as a psychologist, Maslow was influenced by figures such as Alfred Adler and Harry Harlow.
Abraham Maslow continued to make significant contributions to psychology through his research, teaching, and publications. He passed away on June 8, 1970, in Menlo Park, California, leaving behind a legacy of innovation and dedication in the field of humanistic psychology.
Education Background of Abraham Maslow
| Education Level | Details |
| High School | Abraham Lincoln High School, New York; graduated in 1926. |
| Undergraduate | Brooklyn College, 1930 earned a degree in Psychology and Humanities, focusing on psychological theories and human behavior. |
| Master’s Degree | University of Wisconsin, 1931 obtained a Master’s degree in Psychology, studying advanced psychological theories and research methods.hology. |
| Doctorate | University of Wisconsin, 1934 Ph.D. in Psychology with a dissertation on animal behavior studies. |
| Notable Influence | Influenced by the work of John Dewey and Gestalt psychologists, which shaped his humanistic approach. |
Notable Works of Abraham Maslow
Abraham Maslow’s notable works have had a profound impact on psychology, particularly in the areas of human motivation and self-actualization. His research laid the groundwork for understanding human needs and personal development.
Readout comparative table for better understanding:
| Theory/Work | Details | Significance |
| Hierarchy of Needs | Introduced in “Motivation and Personality” (1954). Describes a five-tier model of human needs: physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. | Revolutionized the understanding of human motivation by emphasizing that basic needs must be fulfilled before higher-level psychological needs. |
| Self-Actualization | A core concept describing the realization of one’s potential and achieving personal growth and fulfillment. | Highlighted the importance of striving for personal development and achieving one’s full potential, influencing both psychological theory and personal growth practices. |
| Peak Experiences | Refers to intense moments of joy, creativity, and fulfillment discussed in “Toward a Psychology of Being” (1962) | Provided a framework for understanding extraordinary experiences that contribute to personal growth and psychological well-being. |
| Eupsychian Management | Applied psychological principles to management, advocating for practices that foster employee growth and satisfaction. | Introduced management practices that enhance organizational effectiveness by promoting employee development and well-being. |
| The Psychology of Science | Examined the psychological aspects of scientific thinking and creativity in “The Psychology of Science” (1966). | Offers insights into the psychological processes involved in scientific inquiry and creativity, influencing perspectives on scientific practice and research. |
Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs
It outlines a five-tier model of human needs, arranged in a pyramid shape. The idea is that individuals are motivated to fulfill needs in a specific order, from the most basic to the more complex.
Image Source: bitesizelearning.co.uk
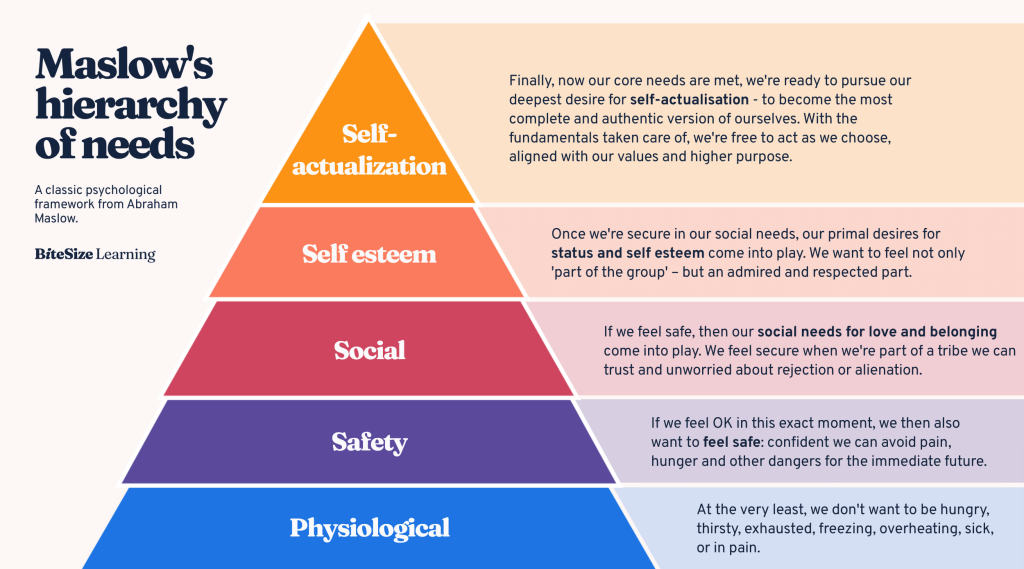
Here’s a breakdown of the levels from bottom to top:
- Physiological Needs: These are the most fundamental requirements for human survival, including air, water, food, shelter, and sleep. Without meeting
- these needs, a person cannot focus on higher-level needs.
- Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security. This includes physical safety, financial stability, health, and protection from accidents and illness.
- Love and Belongingness Needs: With safety needs secured, people seek social relationships, love, and a sense of belonging. This includes intimate relationships, friendships, and connections with groups and communities.
- Esteem Needs: After establishing a sense of belonging, individuals strive for self-esteem and the esteem of others. This encompasses feelings of accomplishment, recognition, and respect, as well as a positive self-image.
- Self-Actualization Needs: At the top of the hierarchy is self-actualization, where individuals focus on personal growth and self-fulfillment. This involves realizing one’s potential, creativity, and pursuing personal goals and aspirations.
Maslow believed that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before they can address higher-level needs. For example, a person who is struggling to meet basic physiological needs is unlikely to be concerned with esteem or self-actualization. The hierarchy provides a framework for understanding human motivation and personal development.
Abraham Maslow’s work had a profound impact on psychology and related fields:
Cultural Impact: Maslow’s research on self-actualization and the hierarchy of needs emphasized the importance of personal growth and fulfillment, influencing humanistic psychology and contributing to a broader understanding of human motivation and well-being.
Academic Institutions: Maslow’s theories, particularly the hierarchy of needs, have been integrated into psychology curricula and continue to shape educational approaches and research methodologies across psychology departments globally.
Famous Books and Publications

Motivation and Personality by Abraham Maslows 1954

Toward a Psychology of Being 1962

The Farther Reaches of Human Nature 1971

The Maslow Business Reader by Abraham Maslows

Maslow on Management by Abraham Maslows 1962

The Humanistic View of Man by Abraham Maslows 1971

Dynamics of Personality Organization 1972

The Psychology of Abraham Maslow
Influence on Contemporary and Future Psychological Research
Abraham Maslow’s influence on contemporary and future psychological research is significant:
- Humanistic Psychology: Maslow’s work laid the foundation for humanistic psychology, which emphasizes the study of the whole person and the importance of personal growth. This approach continues to influence contemporary therapy practices and counseling techniques.
- Positive Psychology: Maslow’s focus on self-actualization and peak experiences has been a precursor to the positive psychology movement. Researchers like Martin Seligman have built upon Maslow’s ideas to explore well-being, happiness, and strengths.
- Motivation Theory: The hierarchy of needs remains a cornerstone in understanding human motivation. Contemporary research on motivation in various domains, including education, work, and health, often references or builds upon Maslow’s framework.
- Self-Determination Theory: Deci and Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) explores similar concepts to Maslow’s hierarchy, such as intrinsic motivation and the role of needs in psychological well-being, extending and refining Maslow’s ideas.
- Organizational Psychology: Maslow’s application of psychological principles to management and organizational practices has influenced modern approaches to leadership, employee motivation, and workplace culture.
Psychologists Influenced by Abraham Maslow

- Carl Rogers: Developed client-centered therapy, emphasizing self-actualization and personal growth, building on Maslow’s concepts of self-fulfillment and human potential.
- Martin Seligman: Founded positive psychology, focusing on well-being and happiness, extending Maslow’s ideas on self-actualization and peak experiences.
- Rollo May: Integrated Maslow’s ideas into existential psychology, exploring creativity and personal growth in the context of existential challenges.
- Erich Fromm: Expanded on Maslow’s concepts of self-actualization, focusing on human freedom and the search for meaning.
- John Stuart Mill: Applied Maslow’s ideas to understand human potential and development, contributing to broader discussions on personal growth.
Legacy of Abraham Maslow
- Educational Approaches: Maslow’s ideas have shaped educational practices by emphasizing the importance of addressing students’ basic needs to foster an environment conducive to learning and personal growth.
- Therapeutic Techniques: Many modern therapeutic approaches incorporate Maslow’s ideas about self-actualization and personal potential, focusing on client strengths and personal growth.
- Human Development: Maslow’s theories contribute to understanding human development stages and the conditions that promote optimal growth and self-fulfillment throughout the lifespan.
- Research on Well-Being: His work has influenced research on wellness and health psychology, advocating for holistic approaches to physical and mental health.
- Influence on Psychologists: Maslow’s ideas have inspired a wide range of psychologists and scholars, shaping various domains of psychological research and practice.
Conclusion
Abraham Maslow’s innovative theories on human motivation and self-actualization have profoundly shaped modern psychology and beyond. His hierarchy of needs and concepts of self-actualization continue to influence therapeutic practices, educational methods, and organizational strategies.
Maslow’s legacy endures through his impact on humanistic psychology, positive psychology, and ongoing research into well-being and personal growth. His work remains a cornerstone for understanding and enhancing human potential across various fields.
FAQs
What role did Maslow’s theory play in the development of positive psychology?
Maslow’s theory played a crucial role in the development of positive psychology by highlighting the importance of self-actualization and peak experiences. His emphasis on personal growth and fulfillment provided a framework for understanding well-being and happiness. These concepts influenced positive psychology’s focus on strengths, resilience, and the pursuit of a meaningful life.
What is the relationship between Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and mental health?
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is closely related to mental health, as it suggests that fulfilling lower-level needs (such as physiological, safety, and belonging) is essential for achieving higher-level psychological well-being. Meeting these foundational needs supports emotional stability and self-actualization, which are crucial for overall mental health.
What are some examples of peak experiences according to Maslow?
According to Maslow, peak experiences are profound moments of joy, creativity, and fulfillment. Examples include achieving a significant personal milestone, experiencing deep connections with others, engaging in creative activities, or having transformative insights. These moments are characterized by a sense of intense satisfaction and transcendence, contributing to personal growth and self-actualization.
How can Maslow’s theories be applied in therapy?
Maslow’s theories can be applied in therapy by focusing on helping clients fulfill their basic needs and work towards self-actualization. Therapists can:
- Foster Personal Growth: Support clients in developing their strengths, pursuing meaningful activities, and achieving their full potential.
- Address Basic Needs: Ensure clients’ physiological, safety, and relational needs are met to create a stable foundation for psychological work.
- Promote Self-Actualization: Encourage clients to set and achieve personal goals, explore their potential, and strive for self-fulfillment.
- Explore Peak Experiences: Help clients identify and cultivate moments of deep joy and creativity to enhance their overall well-being.
References
- [1] Maslow, A. H. (1954). Motivation and personality. Harper & Row.
- [2] Maslow, A. H. (1962). Toward a psychology of being. Van Nostrand Reinhold.
- [3] Maslow, A. H. (1971). The farther reaches of human nature. Viking Press.
- [4] Maslow, A. H. (1962). Self-actualization: A study of psychological health. Harper & Row.
- [5] Maslow, A. H. (1962). The scientific study of personality. Harper & Row.
- [6] Maslow, A. H. (1971). The humanistic view of man. University of Michigan Press.
- [7] Maslow, A. H. (1972). The need for self-actualization. Harper & Row.
- [8] Maslow, A. H. (1968). Creativity in self-actualization. Harper & Row.
- [9] Maslow, A. H. (1966). The psychology of science: A reconnaissance. Harper & Row.
- [10] Rogers, C. R. (1961). On becoming a person: A therapist’s view of psychotherapy. Houghton Mifflin.






